How much information about an employee is enough? Can anyone put a cap on yes we can capture the whole employee data in say 50 Fields.
I started off with 50 fields and in various process of requirement gathering, brainstorming, observing the fields ballooned up to 140 and we were still not sure whether we have the full information.
Although the number of fields depends upon the customer requirement i.e. what they perceive to be as employee information and the number of details the need to capture, and the format in which they need to capture the same… (to be continued)
BagItToday – My Credit
Hey…check this out… I hope its as good as they promise..
OpenTaps CRM/SFA Module
360 degree view of OpenTaps CRM/SFA Module.
Managing Customer Relations
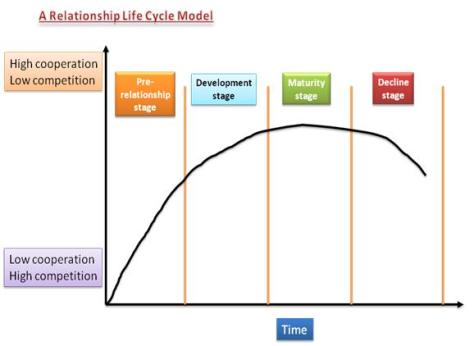
- CRM-Customer Relationship Lifecycle Model
The relationship matrix method is based on the relationship life cycle theory that can be used to determine what priorities should be given in managing customer relationships. To ensure long-term profitability and value creation, a company should focus on building a strong and lasting relationship for continuous growth in terms of value and profit.
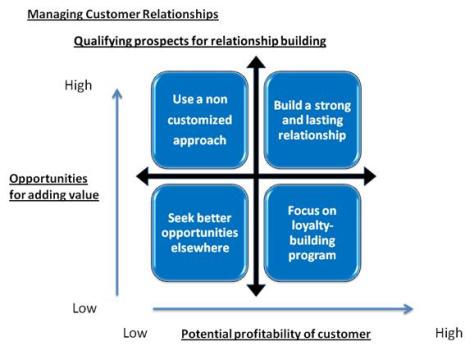
- Qualifying prospects for relationship buildinghip
It has 2 dimensions: Potential profitability of customer and opportunities for adding value. The basic idea behind the matrix is that the customer having highest potential profitability and which gives the highest opportunities for adding value the better it is for the company.
Placing profitability/opportunities in the matrix results in 4 approaches in the qualifying prospects for relationship building of a company:
1. Build a Strong and lasting relationship (=high profitability, high opportunity for adding value).
– use large amounts of cash and are leaders in the business so they
should also generate large amounts of cash.
-Opportunity for adding values is very high. If needed any attempt should be made to acquire or retain the customer, because the rewards will be a very high if a relationship is maintained.
2. Focus on loyalty-building program (=high profitability, low opportunity for adding value).
– Profits and cash generation should be high, and because of the low potential for adding values and growth, investments would be.
3. Use a non customized approach (= low profitability, High opportunity for adding value).
– have the worst relationship characteristics of all, because low potential profitability and high opportunity for adding values.
-avoid and minimize the number of such relationships with a company.
4. Seek better opportunities elsewhere. (=low growth, low market share).
– beware of any new plans for value building.
– Efforts should be made to get out of the relationship as these companies will simply absorb great amounts of time and effort
Some limitations of the Relationship Matrix include:
1. It all depends on the potential profitability with/without considering the dynamic nature of market/client.
2. Sometime the value received from low profitability customers are more than High profitability customer. The values in the form of experience and knowledge transfer.
The QPR (qualifying prospects relationship building) matrix – This graph describes the qualifying prospects for relationship building depending upon the opportunities for adding value and potential profitability of customer from the relationship.
CRM Functionalities
• Sales Force Automation
• Service ( Customer) and Direct Support
• Marketing Automation
• Call Centre Operations(Customer Support)
• E-Commerce, Shopping Cart & Offline Ordering
• Business Analytics
• Real Time visibility
• Email Management
• Affiliate and JV Programs
• Order Management
CRM Modules
A well organised CRM tool should have the following moduels for real time tracking and 360 degree view of the business. The Modules are as mentioned below.
- Lead Management
- Accout Management
- Contact Management
- Marketing Management
- Order Management
- Sales Management
- Dashboard
- Lead Management: A lead is a person or entity, who is potentially interested in purchasing a product or service. A lead represents first stage of sales process. It is also the entry point in a Sales Funnel/Sales Tunnel or sales pipeline. Simply putting it he is a source through which we can get value in terms of money and work.
A lead may come from marketing Lead Generation Process like direct marketing, online marketing, trade shows, internet marketing etc. or through sale prospective i.e. cold call.
For a sales lead to qualify as a sales prospect, qualifciation must be performed and lead be evaluated against a set of standards and bencmarks. This qualificatin involves various steps liek direct interrogation, finance and time frame for the purchase decision.
- Account Management. Once the lead is qualified and converted into an authentic and reliable one. the next step is towards creation of account for the company where lead is the contact person. the tool must give and automatic and real time account number to an individual company. which will act as a sole point of referring to the customer.
- Contact Management. The contact information provided by the Lead can act as a correspondence address as well as the billing address for communication as well as addressing the payment issues. A customer can have two different addresses one each for correspondence and one for Billing.
- Marketing Management. This is a broad field which is beyond the scope a single paragraph. the main purpose of Marketing Management is to target customer/s with proper segmentation for maximum ROI. They segmentation could vary from age, sex, geography, climate etc. This helps in getting new Leads as well as direct business.
- Order Management.
- Sales Management.
- Dashboard.
Challenges Addressed by CRM?
CRM helps in addressing a lot of challenges which are otherwise overlooked by routine business practices for e.g.
1. Lack of a disciplined customer engagement process. This is among the major concerns for lack of customer retention.
Few of the things need to overcome this barrier are Consistent, Repeatable Processes, Systematic and Recurring Approach and Customer-driven Business Strategies.
2. Companies also face lots of difficulty in gathering and sharing customer information which impacts not only External Customer Relations and Internal Communication and Coordination but also makes it a Challenge to turn customer requirements into Desirable Solution Offerings
Determinants of CRM
Trust
The willingness to rely on the ability, integrity, and motivation of one company to serve the needs of the other company as agreed upon implicitly and explicitly.
Value
The ability of a selling organisation to satisfy the needs of the customer at a comparatively lower cost or higher benefit than that offered by competitors and measured in monetary, temporal, functional and psychological terms.
CRM- Customer Relationship Management
CRM is a Strategic Business Process or approach aimed towards creating, developing and enhancing relationship with customer and increase stakeholder/shareholder value. To achieve this we need to target our customer carefully, develop relationship with good service and enhance the value we are getting out of the relationship.There are too many definitions of CRM available online. Varying from person to person, Company to company and in many cases even within in an organization, where different branch seems to have different outlook for the much talked about CRM.
In other terms CRM is aimed towards enhancing the acquisition and retention of profitable customers by respectively, initiating and improving relationship with them.
The content we’ll be sharing here will vary from discussing CRM, exploring Open Source CRM tools or Open Source ERP software’s which also support CRM or SFA. WE will also be exploring the CRM functionality offered by different Open Source tools like OpenTaps, SugarCRM, Compiere, ADempiere etc and comparisons between them.
What we achieve with the help of CRM?
Exchange of value, “Money and trust” is beneficial for both parties in the long run. The need is to extract or maximize the value of desirable customer/segments.
While ERP uses customer and internal information to reduce costs by improving internal operations in back office process related to MRP, SCM, Finance, Manufacturing and Inventory etc.
CRM uses the customer information to increase revenue by enhancing external operations in front office activities which varies from Sales, Marketing and Customer Service and Support over a period of time.
Different Outlook of CRM:
CRM functions are interrelated with each other, working towards a common goal of better customer value generation, retention and success of CRM activities.
1. Front Office: deals with direct customer interaction with the help of IT tools e.g. email online services etc as well as by face to face meeting with the client, phone calls etc.
2. Back Office: deals with the strategic operations of the organization that provides the road map for front office to work on. E.g. Marketing, Sales, Billing, Financials, Planning, Maintenance etc.
3. Business Relationships: is an external network which supports both front as well as back office operations. It involves interaction with client as well as business partners, associations etc.
4. Business Analytics: This function is the key to all strategies which deals with analyzing the CRM data in order to conceive, plan, and act towards future strategies towards increasing profitability and value generation.
Approaches CRM:
There can be various approaches to CRM depending upon the operation, business function, geography, data etc.e.g:
1. Operational CRM
2. Analytical CRM
3. Collaborative CRM
Operational CRM: This supports the front office e.g. sales, marketing, phone calls. Customer interaction history is stored in the respective customer database with the help of Enterprise IT tools
Analytical CRM: It analyzes customer data for a variety of purpose
1. Customer focused approach towards marketing campaigns.
2. For customer acquisition, customer retention, cross-selling & up-selling etc.
3. Pricing and product development towards anticipating customer behaviour and service offering.
4. Financial forecasting, customer profitibality analysis.
5. Value proposition for the customer and self.
Collaborative CRM: It is a portal where different department of an organization can share information related to customer for working towards customer support and service.
The two major IT components for CRM are
1. Data Repository- required for collecting data, filter, organize, and analyzing customer data.
2. Application’s – Which adds value and improves the interaction and exchange of dialogues with customer.
WILL BE FINISHING THE ANALYSIS SHORTLY!!!!!!!!!!!!!